High Pressure Mercury Vapour Lamp Working Principle

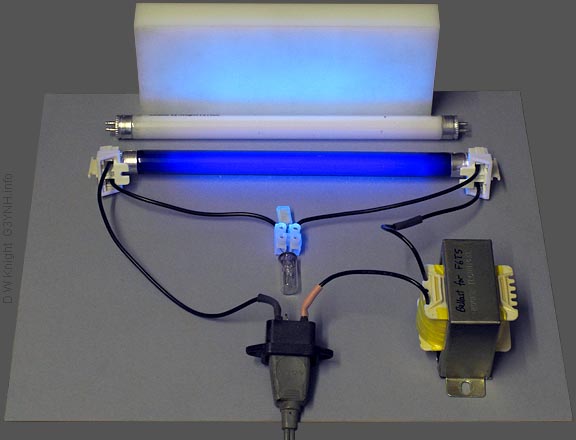
Lamps of today are high pressure lamps with a fused quartz inner discharge tube.
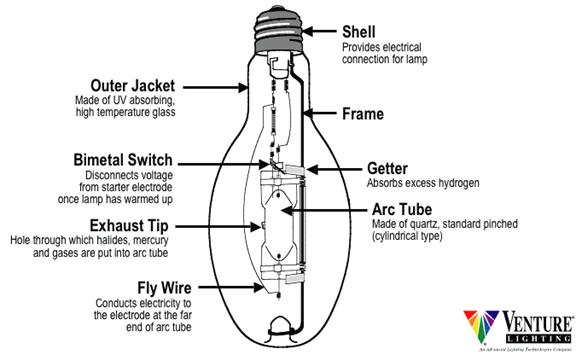
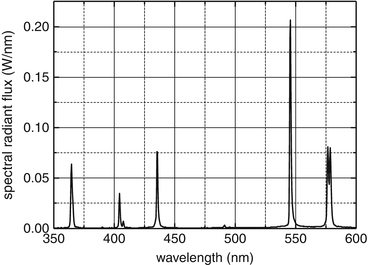
High pressure mercury vapour lamp working principle. Hot cathode lamps have electrodes that operate at a high temperature and are heated by the arc current in the lamp. Developed in the 1960s they are similar to mercury vapor lamps but contain additional metal halide compounds in the quartz arc tube. The lps lamp is also called a sox lamp so for sodium advantages. A mercury vapor lamp is a gas discharge lamp that uses an electric arc through vaporized mercury to produce light the arc discharge is generally confined to a small fused quartz arc tube mounted within a larger borosilicate glass bulb.
The heat knocks electrons out of the electrodes by thermionic emission which helps maintain the arc in many types the electrodes consist of electrical filaments made of. The outer bulb may be clear or coated with a phosphor. After that the lamp would heat fast and mercury became a vapor. The high pressure helps increase efficiency and this was developed in 1936 35 years after the low pressure lamps came out.
Lamps are divided into families based on the pressure of gas and whether or not the cathode is heated. Two varieties of such lamps exist. A metal halide lamp is an electrical lamp that produces light by an electric arc through a gaseous mixture of vaporized mercury and metal halides compounds of metals with bromine or iodine it is a type of high intensity discharge hid gas discharge lamp. The energy used to make non visible light is a waste of energy since it does not help do the principle job of an electric light.
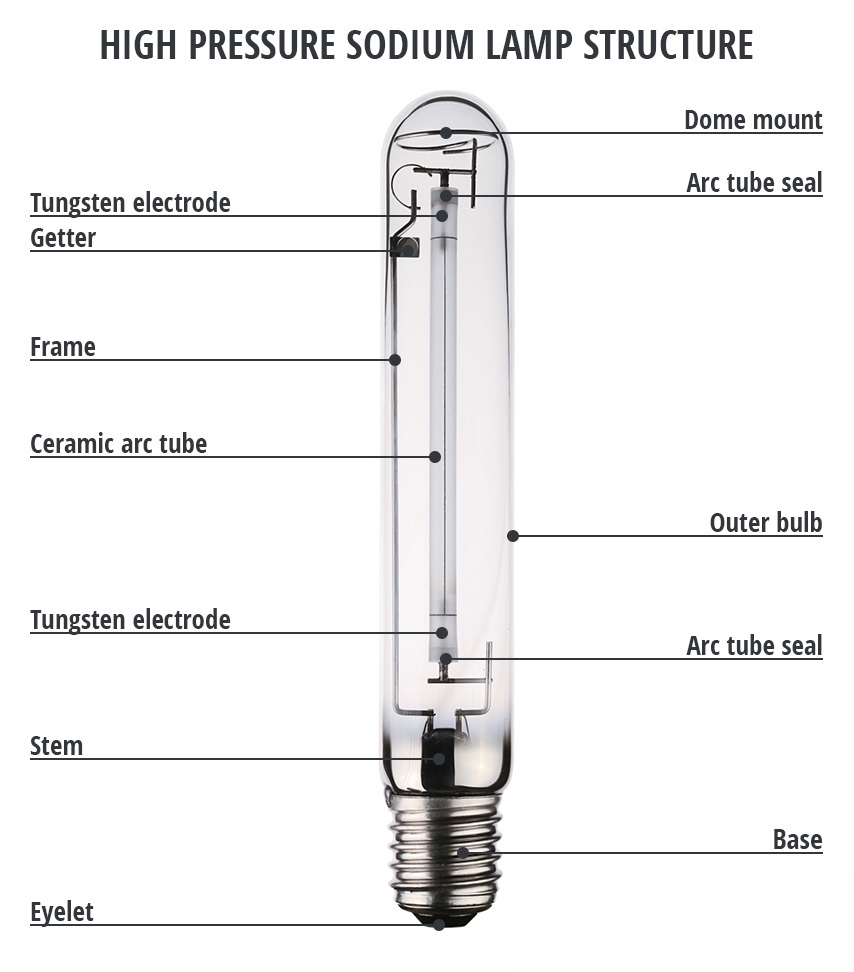
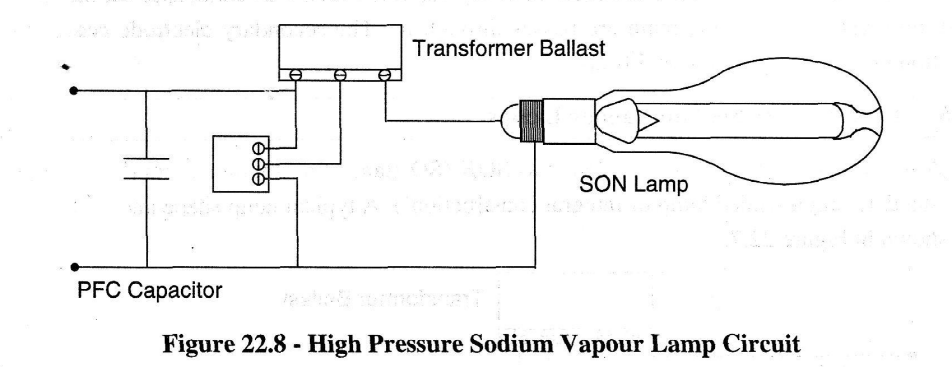
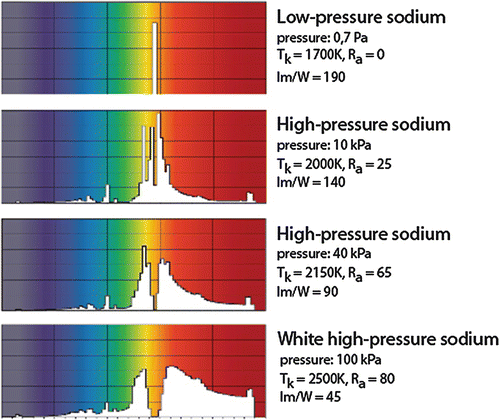
High pressure sodium lamp hps lamp. A sodium vapor lamp is a gas discharge lamp that uses sodium in an excited state to produce light at a characteristic wavelength near 589 nm. In either case the outer bulb provides thermal insulation protection from the ultraviolet radiation the.